Varicose Veins
Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for Healthier Veins
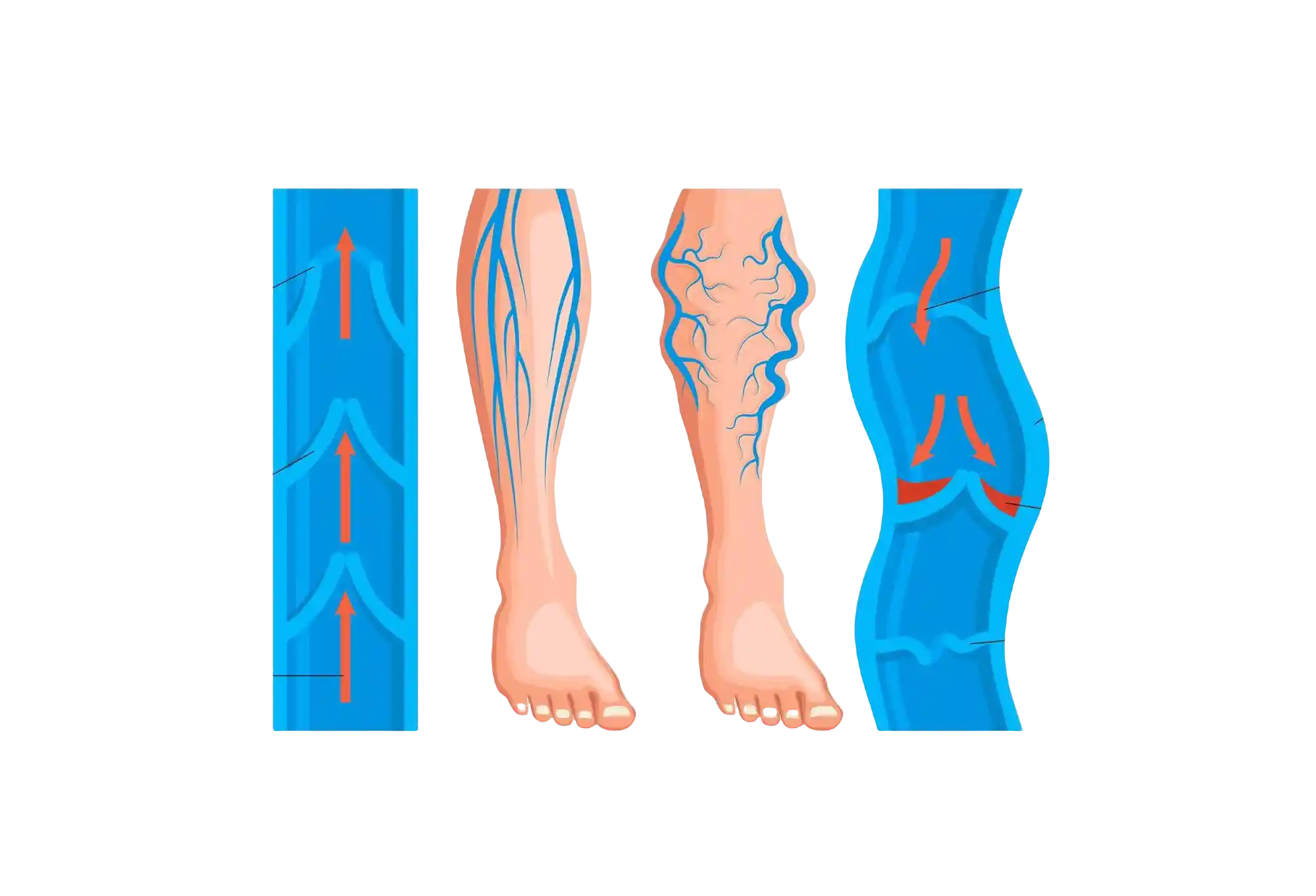
What are Varicose Veins?
Varicose Veins are enlarged, twisted veins that often appear blue or purple beneath the skin. They occur when valves in the veins malfunction, causing blood to pool instead of flowing efficiently back to the heart. While commonly affecting the legs, varicose veins can develop in other parts of the body as well. Though they are often a cosmetic concern, severe cases can lead to discomfort and complications.
Key Features of Varicose Veins
- Usually appear as bulging, rope-like veins under the skin
- Commonly found in the legs and feet due to pressure from standing or walking
- Associated with a heavy or aching sensation in the affected area
- Can cause swelling, itching, and skin discoloration
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Symptoms vary from person to person and may include:
- Visible, twisted, and bulging veins
- Aching or heavy feeling in the legs
- Swelling in the lower legs or ankles
- Itching around the affected veins
- Cramping, throbbing, or burning sensations in the legs
- Skin discoloration or hardening near the veins in severe cases
Causes and Risk Factors
Varicose veins develop when the valves in the veins weaken or fail. Contributing factors include:
- Age: Risk increases as veins lose elasticity with age
- Gender: More common in women due to hormonal changes
- Pregnancy: Increased blood volume and pressure during pregnancy
- Obesity: Extra weight puts additional pressure on veins
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Limits blood flow in the legs
- Family History: Genetic predisposition to weak vein valves
How are Varicose Veins Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis involves physical examination and imaging studies:
- Ultrasound: Assesses blood flow and identifies damaged valves
- Venography: Uses contrast dye to visualize vein abnormalities
Treatment options range from lifestyle changes to minimally invasive procedures:
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, elevating the legs, and maintaining a healthy weight
- Compression Stockings: Improve circulation and reduce swelling
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of a solution to close smaller veins
- Endovenous Laser Ablation: A laser treatment to seal larger veins
- Surgical Ligation and Stripping: Removal of severely damaged veins
Risks and Potential Complications
If untreated, varicose veins can lead to:
- Chronic pain and discomfort
- Skin ulcers near the ankle
- Superficial thrombophlebitis: Blood clots in surface veins
- Bleeding from ruptured veins
- Venous insufficiency: Poor blood return to the heart
Recovery and Long-Term Management
Steps to manage varicose veins and reduce recurrence include:
- Using compression stockings as directed
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Elevating the legs to reduce swelling
- Avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting
- Seeking regular follow-ups for vein health assessments
With proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments, most individuals experience significant symptom relief and improved quality of life.