Spinal AVM
Understanding Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations
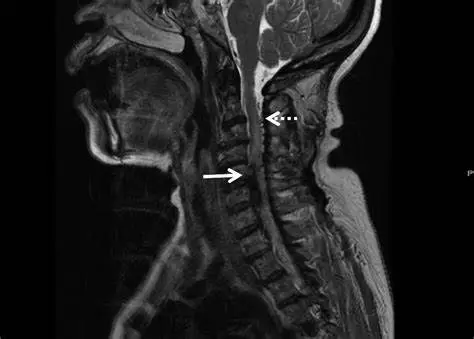
What is Spinal AVM?
A Spinal AVM (Spinal Arteriovenous Malformation) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels located within or around the spinal cord. These malformations disrupt the normal flow of blood between arteries and veins, potentially causing reduced oxygen delivery to the spinal cord. Over time, this can lead to progressive damage or sudden neurological symptoms if the AVM ruptures, causing bleeding (hemorrhage).
Key Differentiators
- Abnormal connection between arteries and veins in the spinal cord
- May remain asymptomatic for years
- High risk of hemorrhage, causing neurological damage
- Often diagnosed through advanced imaging techniques like MRI or angiography
Symptoms
The symptoms of a spinal AVM depend on its size, location, and whether it has ruptured. Common symptoms include:
- Progressive weakness or numbness in the legs
- Back pain or localized discomfort
- Loss of bowel or bladder control
- Sudden onset of severe pain and paralysis (if a rupture occurs)
- Muscle weakness or spasticity
- Reduced sensation or tingling in the limbs
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of spinal AVMs is often unknown, but they are believed to arise during fetal development. Some factors and conditions associated with spinal AVMs include:
- Congenital Factors: Malformations present at birth
- Hereditary Disorders: Such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT)
- Trauma: Damage to spinal blood vessels may contribute in rare cases
- Infections: Certain infections may cause vascular abnormalities
Diagnosis
Diagnosing spinal AVMs involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies to confirm the presence of abnormal blood vessels. Common diagnostic tools include:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of the spinal cord and surrounding tissues
- MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography): Used to visualize blood flow and detect abnormalities
- Spinal Angiography: A catheter-based procedure to map the blood vessels in the spine
Treatment Options
The treatment of spinal AVMs depends on factors such as the patient's symptoms, the size and location of the AVM, and the risk of rupture. Common treatments include:
- Embolization: A minimally invasive procedure where a catheter is used to inject a substance into the AVM to block blood flow and reduce its size.
- Surgical Resection: Removal of the AVM through microsurgery. This is often used for accessible and symptomatic AVMs.
- Radiosurgery: A non-invasive procedure that uses focused radiation to close off the abnormal vessels over time.
- Observation: For small, asymptomatic AVMs, doctors may recommend monitoring the condition through regular imaging.
What to Expect as a Patient
Living with a spinal AVM can be challenging, but early diagnosis and treatment greatly improve outcomes. Patients may experience:
- Improved quality of life after successful treatment
- Temporary discomfort following surgical or endovascular procedures
- Ongoing monitoring to ensure the AVM does not recur or worsen
- Physical therapy to regain mobility and strength if neurological symptoms were present
A multidisciplinary care team, including neurosurgeons, neurologists, and rehabilitation specialists, plays a key role in recovery.