Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Recognizing, Preventing, and Treating DVT
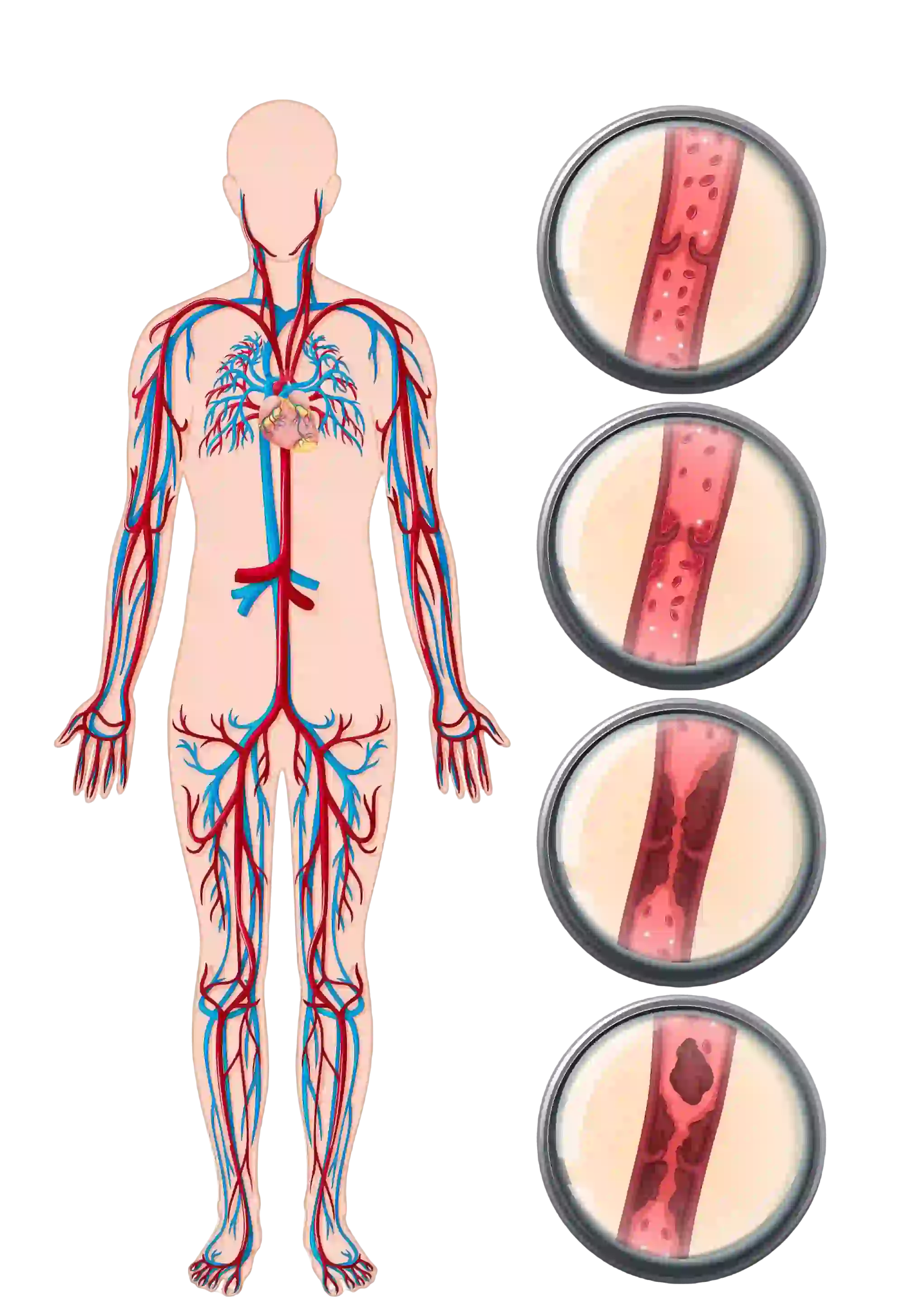
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. This condition can cause swelling, pain, and complications if the clot travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE). Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent severe complications.
Key Features of DVT
- Commonly affects veins in the lower legs and thighs
- Caused by slow or restricted blood flow, clotting disorders, or injury to the vein
- Can be life-threatening if untreated due to the risk of pulmonary embolism
- Symptoms may vary from mild to severe or even asymptomatic
Symptoms of DVT
Some individuals with DVT may not experience symptoms. When symptoms occur, they may include:
- Swelling in one leg (or arm in rare cases)
- Pain or tenderness, especially when standing or walking
- Red or discolored skin over the affected area
- Warmth in the affected area
- Visible surface veins appearing larger than usual
Causes and Risk Factors
DVT occurs when blood clots form in the deep veins due to:
- Immobility: Prolonged sitting, bed rest, or long flights
- Injury: Trauma to the vein or surrounding tissue
- Surgery: Postoperative immobility increases the risk
- Clotting Disorders: Genetic or acquired conditions affecting blood clotting
- Pregnancy: Increased clotting tendency during and after pregnancy
- Obesity: Extra pressure on veins increases the risk
How is DVT Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination and imaging:
- D-Dimer Test: Measures clotting activity in the blood
- Ultrasound: Detects clots in the deep veins
- Venography: X-ray imaging with contrast dye for detailed clot visualization
Treatment aims to prevent clot growth and complications:
- Anticoagulants: Blood thinners to prevent clot formation and growth
- Compression Stockings: Reduce swelling and prevent post-thrombotic syndrome
- Thrombolysis: Dissolves larger clots in severe cases
- IVC Filter: Filters placed in the inferior vena cava to prevent clots from reaching the lungs
Risks and Potential Complications
If untreated, DVT can lead to severe complications such as:
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A life-threatening condition caused by the clot traveling to the lungs
- Post-Thrombotic Syndrome: Chronic swelling and pain in the affected limb
- Recurrent DVT: Higher risk of future clots
- Venous Insufficiency: Long-term damage to vein valves
Recovery and Long-Term Management
Patients can improve their outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence by:
- Taking prescribed anticoagulants as directed
- Maintaining physical activity to improve blood flow
- Wearing compression stockings as recommended
- Regular follow-up with healthcare providers to monitor progress
- Making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and quitting smoking
With proper treatment and prevention strategies, most patients recover well and reduce their risk of complications.