Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO)
Advanced Care for Complete Coronary Artery Blockage
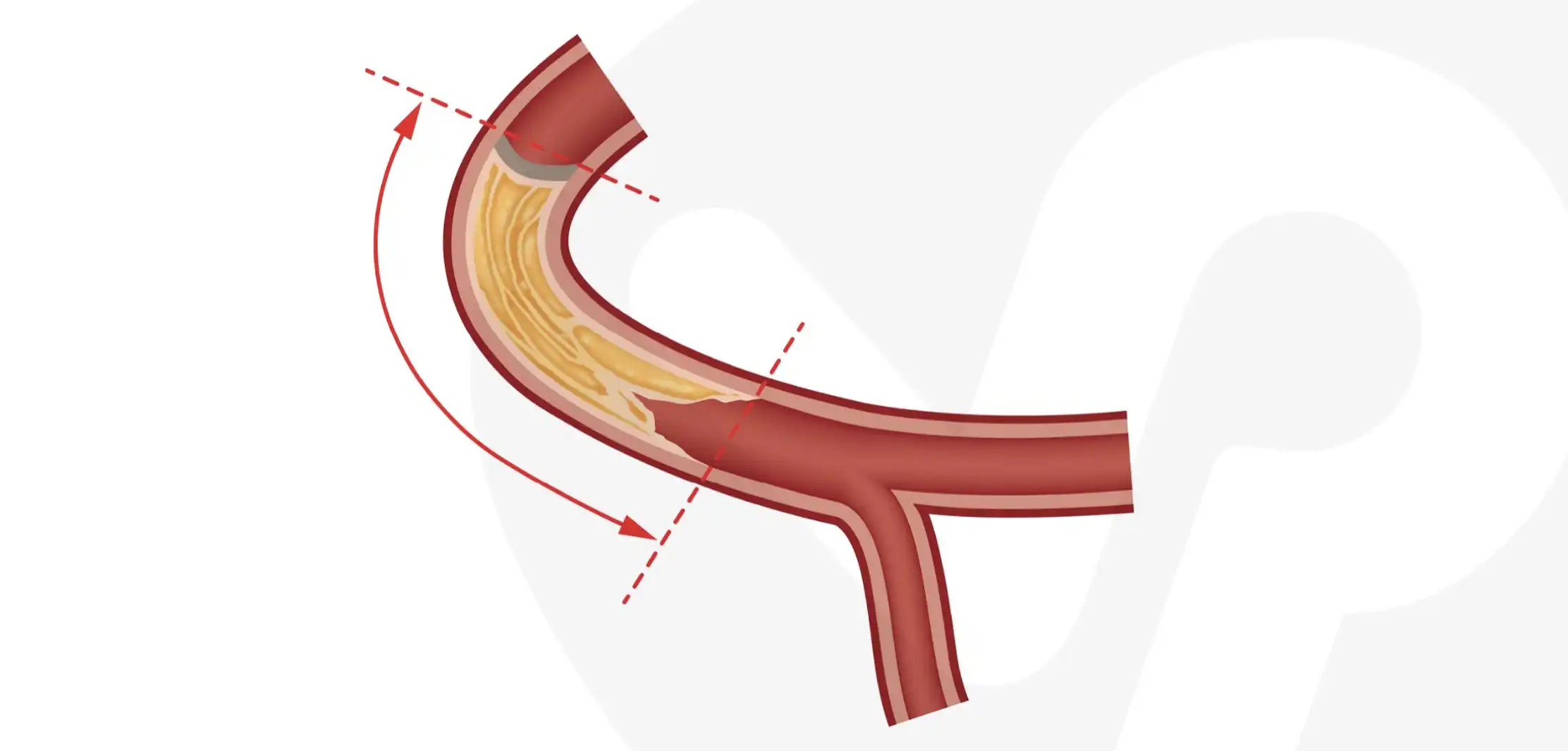
What is Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO)?
Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) is a severe form of coronary artery disease where one or more coronary arteries are completely blocked for 3 months or longer. This blockage is caused by plaque buildup, resulting in restricted blood flow to the heart. CTO can lead to symptoms like chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath and may require specialized treatment to restore blood flow.
Key Features of CTO
- Complete blockage of a coronary artery
- Typically caused by long-standing plaque buildup
- Associated with chronic symptoms of ischemia or reduced blood flow
- Requires specialized techniques for treatment
Symptoms of Chronic Total Occlusion
Symptoms of CTO can vary depending on the severity and extent of the blockage. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent or recurring chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Fatigue and reduced exercise tolerance
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats
- Silent ischemia, where no symptoms are felt but the heart is still affected
Causes and Risk Factors
CTO is primarily caused by the same factors that contribute to coronary artery disease, including:
- Atherosclerosis: Plaque buildup in the arteries
- High Cholesterol: Promotes plaque formation
- Hypertension: Causes damage to blood vessels over time
- Diabetes: Increases the risk of arterial blockages
- Smoking: Damages the blood vessel lining
- Obesity: Linked to multiple cardiovascular risk factors
- Family History: Genetic predisposition to coronary artery disease
How is CTO Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis involves imaging and functional studies to assess the extent of the blockage:
- Stress Testing: Evaluates the heart’s response to physical or pharmacological stress
- Coronary Angiography: Provides detailed images of coronary arteries
- CT Angiography: Non-invasive imaging to detect blockages
Treatment focuses on restoring blood flow and managing symptoms:
- Medications: Includes anti-anginal drugs, cholesterol-lowering medications, and blood thinners
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): A minimally invasive procedure using specialized techniques to open the blocked artery
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): A surgical option for cases unsuitable for PCI
- Hybrid Procedures: Combines open surgery with catheter-based interventions for complex cases
Risks and Potential Complications
While CTO treatments are generally safe, potential complications include:
- Bleeding or infection at the catheter insertion site
- Damage to coronary arteries during intervention
- Kidney injury from contrast dye used in imaging
- Re-blockage of the treated artery (restenosis)
- Rare cases of heart attack or arrhythmia during the procedure
Recovery and Long-Term Management
Recovery after CTO treatment involves a combination of lifestyle changes and ongoing medical care:
- Light activity and gradual return to normal routines
- Medications to prevent clotting and manage heart health
- Regular follow-up visits and imaging to monitor artery function
- Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including diet and exercise
- Participation in cardiac rehabilitation programs
With advanced treatment options, most patients experience improved symptoms and quality of life after CTO interventions.