Cardiac Ablation
Effective Treatment for Irregular Heart Rhythms
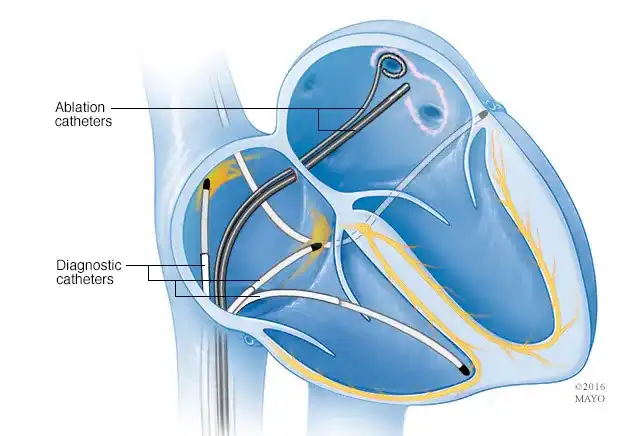
What is Cardiac Ablation?
Cardiac Ablation is a medical procedure used to treat irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias, by targeting and destroying small areas of heart tissue that cause abnormal electrical signals. This minimally invasive technique helps restore normal heart rhythm and is often recommended for patients whose arrhythmias cannot be managed with medication alone.
Key Features of Cardiac Ablation
- Minimally invasive procedure performed under imaging guidance
- Targets the source of abnormal electrical signals in the heart
- Effective in treating atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, and other arrhythmias
- Often performed as an outpatient or same-day procedure
When is Cardiac Ablation Needed?
Cardiac ablation is recommended for patients experiencing:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Irregular and rapid heart rhythm
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): Fast heart rhythm originating above the ventricles
- Ventricular Tachycardia: Life-threatening fast rhythm originating in the ventricles
- Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome: Extra electrical pathway in the heart
- Symptomatic Arrhythmias: Causing palpitations, shortness of breath, or dizziness
- Drug-Resistant Arrhythmias: When medications fail to control symptoms
How is Cardiac Ablation Performed?
The procedure is conducted by an electrophysiologist using advanced techniques:
- Catheter Insertion: Thin, flexible tubes are inserted through veins or arteries, typically in the groin or neck.
- Mapping: Advanced imaging and electrical mapping locate the source of abnormal signals.
- Ablation: Heat (radiofrequency) or cold (cryoablation) is used to destroy targeted tissue.
- Confirmation: The heart rhythm is monitored to ensure successful treatment.
Benefits of Cardiac Ablation
Cardiac ablation offers several advantages, including:
- Restores normal heart rhythm, improving quality of life
- Reduces or eliminates the need for long-term medication
- Minimally invasive with quick recovery time
- Significant symptom relief for patients with severe arrhythmias
- Improves long-term heart function and reduces stroke risk in AFib patients
Risks and Potential Complications
While cardiac ablation is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Bleeding or infection at the catheter insertion site
- Damage to blood vessels or heart tissue
- Rarely, worsening arrhythmias or new arrhythmias
- Blood clots or stroke
- Damage to nearby structures, such as the esophagus in left atrial ablation
Recovery and Long-Term Management
Recovery from cardiac ablation involves:
- Monitoring in a hospital setting for a few hours or overnight
- Resuming light activities within a few days and full activity within a week
- Follow-up visits to ensure the heart rhythm is stable
- Medications to prevent blood clots or manage temporary symptoms
- Adhering to a heart-healthy lifestyle, including diet and exercise
Many patients experience long-term symptom relief and improved heart function following cardiac ablation.