Brain Aneurysm
An In-Depth Guide to Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
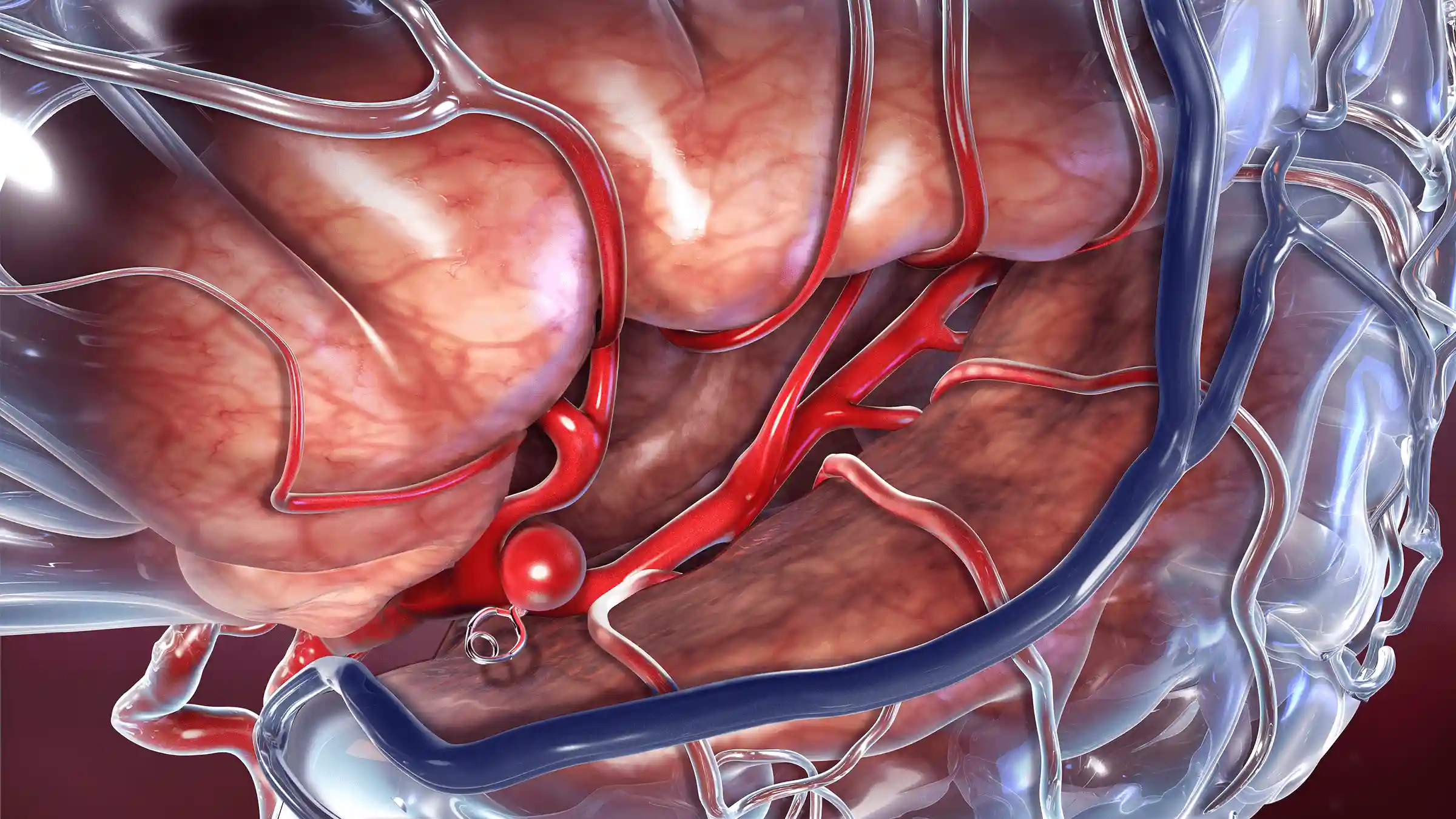
What is a Brain Aneurysm?
A Brain Aneurysm, also known as an intracranial aneurysm, is a localized, balloon-like bulge in a blood vessel in the brain. This occurs due to a weakened section of the vessel wall, which can expand under the pressure of blood flow. Aneurysms may go unnoticed for years, but when they rupture, they cause severe bleeding, known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage, which can be life-threatening.
Key Differentiators
- A localized weakness in the vessel wall causes the bulge
- Small aneurysms may remain asymptomatic
- Ruptured aneurysms are a medical emergency
- Requires a multidisciplinary approach for diagnosis and management
Symptoms
Brain aneurysms are often silent until they rupture. However, in some cases, unruptured aneurysms may press on nearby tissues or nerves, causing symptoms. These include:
- Severe headaches, often described as "the worst headache of your life" during rupture
- Blurred or double vision
- Pain behind the eyes
- Neck stiffness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of brain aneurysms is not always clear, but certain factors can increase the likelihood of their development:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Smoking, which damages blood vessel walls
- Family history of aneurysms
- Head injuries or trauma
- Congenital disorders, such as polycystic kidney disease or connective tissue disorders
- Infections or inflammation of blood vessels
- Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries)
Treatment Options
Treatment for a brain aneurysm depends on its size, location, and whether it has ruptured. The main goals of treatment are to prevent rupture or manage complications after a rupture. Common interventions include:
- Observation: Small, unruptured aneurysms may not require immediate intervention and are monitored regularly through imaging.
- Endovascular Coiling: A minimally invasive procedure where coils are inserted into the aneurysm to block blood flow and reduce the risk of rupture.
- Surgical Clipping: A procedure where a small metal clip is placed at the base of the aneurysm to isolate it from blood circulation.
- Flow Diversion: A newer technique that involves placing a stent-like device in the artery to redirect blood flow away from the aneurysm.
The Surgical Process
For cases requiring surgery, the approach depends on the aneurysm's location and complexity. Here's an overview of the most common procedures:
- Surgical Clipping: Performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon opens a small section of the skull (craniotomy) to access the aneurysm and place a titanium clip across its base.
- Endovascular Procedures: This involves threading a catheter through the femoral artery in the groin to the brain, using imaging to guide the placement of coils or stents.
What to Expect as a Patient
Patients undergoing treatment for brain aneurysms often report:
- Anxiety and fear due to the life-threatening nature of the condition
- Temporary discomfort following invasive procedures
- Improved peace of mind after successful treatment
- In some cases, minor memory or cognitive challenges during recovery
Post-treatment, patients are encouraged to adopt a healthier lifestyle to reduce the risk of recurrence or complications.